Preface
Viglet Turing ES (https://viglet.com/turing) is an open source solution (https://github.com/openviglet), which has Semantic Navigation and Chatbot as its main features. You can choose from several NLPs to enrich the data. All content is indexed in Solr as search engine.
1. Architecture
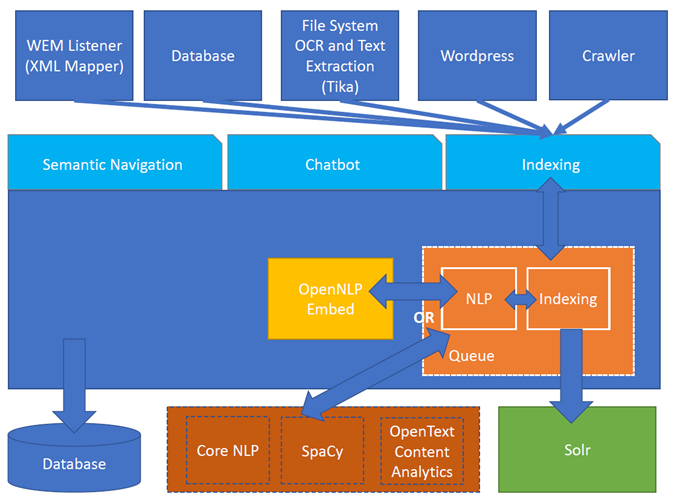
2. NLP
Turing support the followings providers:
2.1. OpenNLP
Apache OpenNLP is a machine learning based toolkit for the processing of natural language text.
Website: https://opennlp.apache.org/
2.2. OpenText Content Analytics
It transforms data into insights for better decision-making and information management while freeing up resources and time.
Website: https://www.opentext.com/
2.3. CoreNLP
CoreNLP is your one stop shop for natural language processing in Java! CoreNLP enables users to derive linguistic annotations for text, including token and sentence boundaries, parts of speech, named entities, numeric and time values, dependency and constituency parses, coreference, sentiment, quote attributions, and relations. CoreNLP currently supports 6 languages: Arabic, Chinese, English, French, German, and Spanish.
Website: https://stanfordnlp.github.io/CoreNLP/,
2.4. SpaCy
It is a free open-source library for Natural Language Processing in Python. It features NER, POS tagging, dependency parsing, word vectors and more.
Website: https://spacy.io
2.5. Polyglot NLP
Polyglot is a natural language pipeline that supports massive multilingual applications.
Website: https://polyglot.readthedocs.io
3. Documents and OCR
It can read PDFs and Documents and convert to plain text and also it uses OCR to detect text in images and images into documents.
4. Semantic Navigation
4.1. Connectors
Semantic Navigation uses Connectors to index the content from many sources.
4.1.1. Apache Nutch
Plugin for Apache Nutch to index content using crawler.
Learn more at https://docs.viglet.com/turing/connectors/#nutch
4.1.2. Database
Command line that uses the same concept as sqoop (https://sqoop.apache.org/), to create complex queries and map attributes to index based on the result.
Learn more at https://docs.viglet.com/turing/connectors/#database
4.1.3. File System
Command line to index files, extracting text from files such as Word, Excel, PDF, including images, through OCR.
Learn more at https://docs.viglet.com/turing/connectors/#file-system
4.1.4. OpenText WEM Listener
OpenText WEM Listener to publish content to Viglet Turing.
Learn more at https://docs.viglet.com/turing/connectors/#wem
4.1.5. Wordpress
Wordpress plugin that allows you to index posts.
Learn more at https://docs.viglet.com/turing/connectors/#wordpress
4.2. Named Entity Recognition (NER)
With NLP it is possible to detect entities such as:
-
People
-
Places
-
Organizations
-
Money
-
Time
-
Percentage
4.3. Facets
Define attributes that will be used as filters for your navigation, consolidating the total content in your display
4.4. Targeting Rules
Through attributes defined in the contents, it is possible to use them to restrict their display based on the user’s profile.
4.5. SDK Java
Java API (https://github.com/openviglet/turing-java-sdk) facilitates the use and access to Viglet Turing ES, without the need for consumer search content with complex queries.
5. Chatbot
Communicate with your client and elaborate complex intents, obtain reports and progressively evolve your interaction.
Its components:
5.1. Agent
Handles conversations with your end users. It is a natural language processing module that understands the nuances of human language
5.2. Intent
An intent categorizes an end user’s intention for taking a conversation shift. For each agent, you define several intents, where your combined intents can handle a complete conversation.
5.3. Actions
The field of action is a simple field of convenience that helps to execute logic in the service.
5.4. Entity
Each intent parameter has a type, called an entity type, that dictates exactly how the data in an end user expression is extracted.
5.5. Training
Defines and corrects intents.
5.6. History
Shows the conversation history and reports.
6. OpenText Blazon Integration
Turing ES detects Entities of OpenText Blazon Documents using OCR and NLP, generating Blazon XML to show the entities into document.
7. Turing ES Console
Turing ES has many components: Search Engine, NLP, Converse (Chatbot), Semantic Navigation
7.1. Login
When access the Turing ES, appear a login page. For default the login/password is admin/admin
7.2. Search Engine
7.2.1. Configuration
Search Engine is used by Turing to store and retrieve data of Converse (Chatbot) and Semantic Navigation Sites.
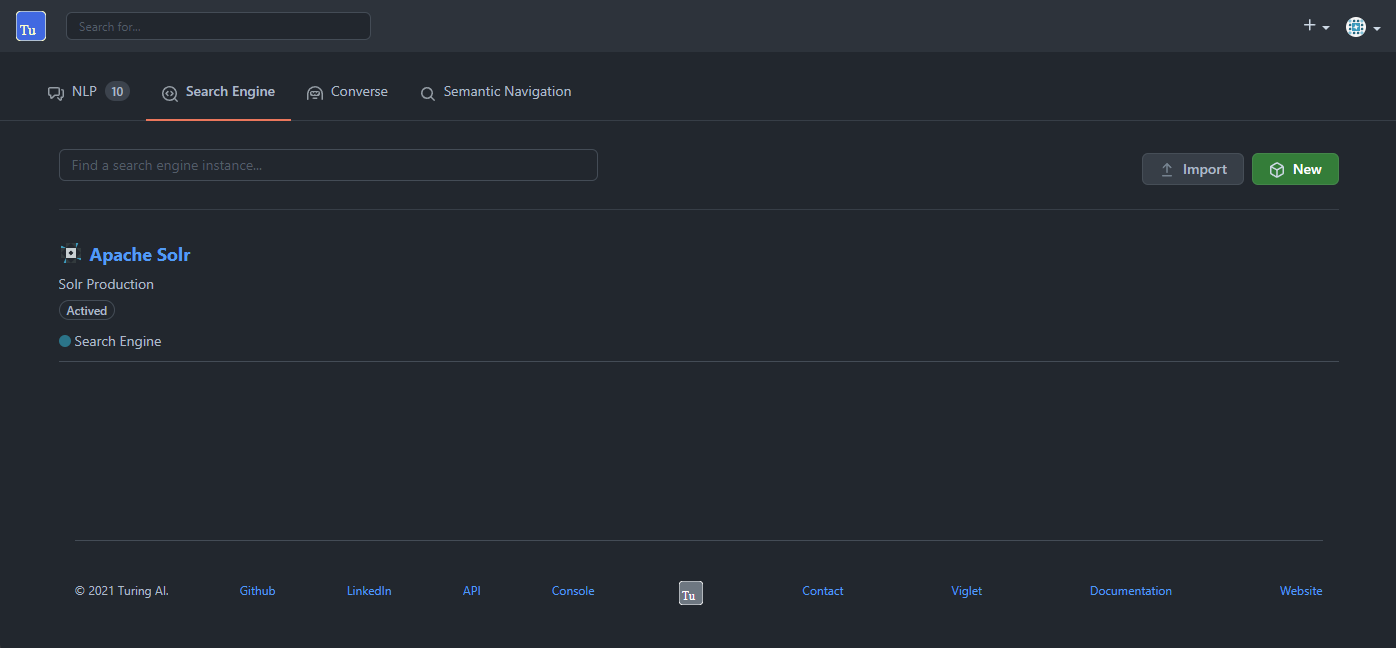
It is possible create or edit a Search Engine with following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of Search Engine |
Description |
Description of Search Engine |
Vendor |
Select the Vendor of Search Engine. For now it only supports Solr. |
Host |
Host name where the Search Engine service is installed |
Port |
Port of Search Engine Service |
Enabled |
If the Search Engine is enabled. |
7.3. Semantic Navigation
7.3.1. Configuration
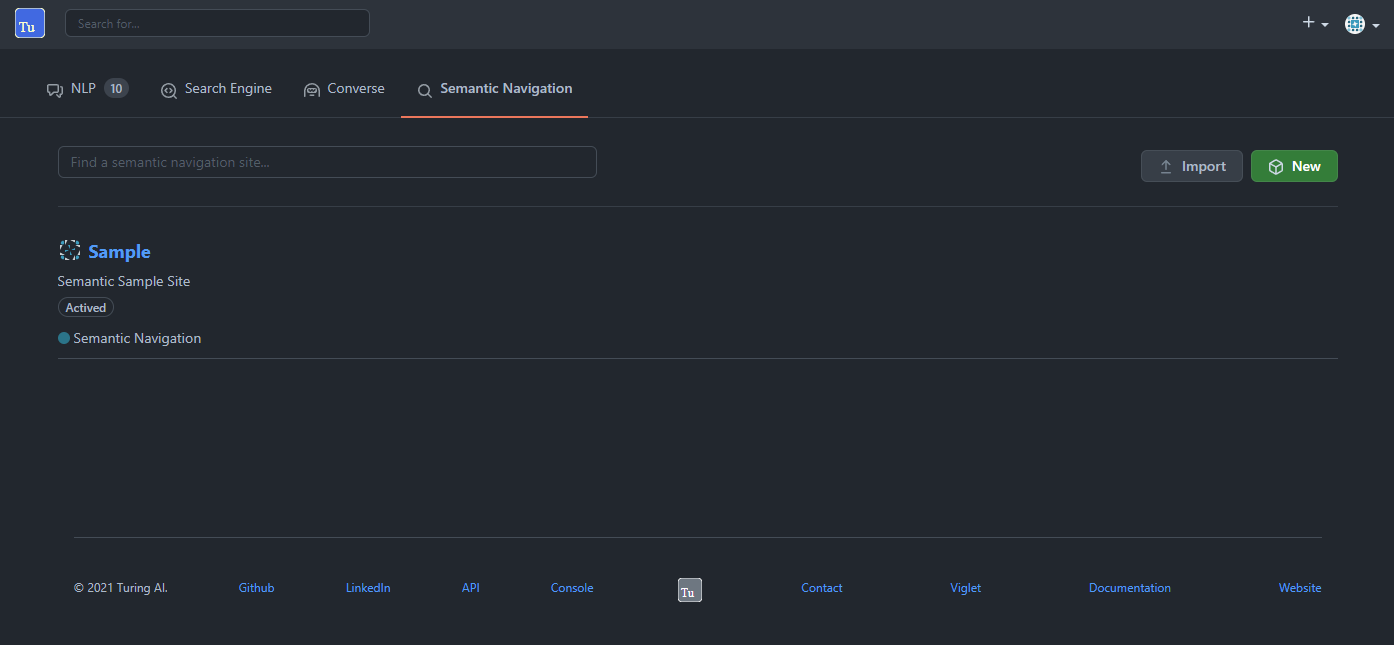
Settings Tab
The Settings of Semantic Navigation Site contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of Semantic Navigation Site. |
Description |
Description of Semantic Navigation Site. |
Search Engine |
Select the Search Engine that was created in Search Engine Section. The Semantic Navigation Site will use this Search Engine to store and retrieve data. |
NLP Vendor |
NLP Vendor for this site. |
Thesaurus |
If will use Thesaurus. |
Multi Languages Tab
The Multi Languages of Semantic Navigation Site contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Language |
Language for Semantic Navigation SIte. |
NLP Instance |
NLP Instance to detect entities during indexing. |
Core |
Solr Core Name to store and to search indexed content. |
Behavior Tab
Contains the following attributes:
| Section | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
Behavior |
Number of items per page |
Number of items that will appear in search. |
Facet |
Facet enabled |
If it will be show Facet (Filters) on search. |
Number of items per facet |
Number of items that will appear in each Facet (Filter). |
|
Highlighting |
Highlighting enabled |
Define whether to show highlighted lines. |
Pre Tag |
HTML Tag that will be used on begin of term. For example: <mark> |
|
Post Tag |
HTML Tag that will be used on the end of term. For example: </mark> |
|
Did you mean? |
"Did you mean?" enabled |
Use "did you mean?" feature. |
Always show the search with the corrected term. |
If the term is misspelled, it already shows the search with the corrected term. If disabled, it shows the search with the entered term in the search. |
|
MLT |
More Like This enabled? |
Define whether to show MLT |
Default Fields |
Title |
Field that will be used as title that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
Text |
Field that will be used as title that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
|
Description |
Field that will be used as description that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
|
Date |
Field that will be used as date that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
|
Image |
Field that will be used as Image URL that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
|
URL |
Field that will be used as URL that is defined in Solr schema.xml |
Merge Providers Details Tab
Merge Providers Details Tab contains the following attributes: .Semantic Navitation Site Merge Providers Attributes
| Section | Attribute | Description |
|---|---|---|
Providers |
Source |
Name of Source Provider. |
Destination |
Name of Destination Provider. |
|
Relations |
Source |
Relation Identifier of Source Provider. |
Destination |
Relation Identifier of Destination Provider. |
|
Description |
Description |
More about merge providers. |
Overwritten Fields |
Name |
Name of Source Field that overwritten destination field or create new one. |
Fields Tab
Fields Tab contains a table with the following columns: .Semantic Navitation Site Fields Columns
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
Type |
Type of Field. It can be: - NER (Named Entity Recognition) used by NLP. - Seach Engine used by Solr. |
Field |
Name of Field. |
Enabled |
If the field is enabled or not. |
MLT |
If this field will be used in MLT. |
Facets |
To use this field like a facet (filter) |
Highlighting |
If this field will show highlighted lines. |
NLP |
If this field will be processed by NLP to detect Entities (NER) like People, Organization and Place. |
When click in Field appear a new page with Field Details with the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Name of Field |
Description |
Description of Field |
Type |
Type of Field. It can be: |
Multi Valued |
If is a array |
Facet Name |
Name of Label of Facet (Filter) on Search Page. |
Facet |
To use this field like a facet (filter) |
Highlighting |
If this field will show highlighted lines. |
MLT |
If this field will be used in MLT. |
Enabled |
If the field is enabled. |
Required |
If the field is required. |
Default Value |
Case the content is indexed without these field, that is the default value. |
NLP |
If this field will be processed by NLP to detect Entities (NER) like People, Organization and Place. |
Spotlight Details Tab
Spotlight Details Tab contains the following attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
Name |
Spotlight Name |
Description |
Spotlight Description |
Terms |
If any of these terms are searched for, this will trigger documents to display as spotlights. |
Indexed Documents |
These documents will display as spotlights when there are search terms. |
7.3.2. Search Page
HTML
In Turing ES Console > Semantic Navigation > <SITE_NAME> > Multi languages > click in Open Search button of some language.
It will open a Search Page that uses the pattern:
GET http://localhost:2700/sn/<SITE_NAME>
JSON
This page requests the Turing Rest API via AJAX. For example, to return all results of Semantic Navigation Site in JSON Format:
GET http://localhost:2700/api/sn/<SITE_NAME>/search?p=1&q=*&sort=relevance
| Attribute | Required / Optional | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
q |
Required |
Search Query. |
q=foo |
p |
Required |
Page Number, first page is 1. |
p=1 |
sort |
Required |
Sort values: |
sort=relevance |
fq[] |
Optional |
Query Field. Filter by field, using the following pattern: FIELD: VALUE. |
fq[]=title:bar |
tr[] |
Optional |
Targeting Rule. Restrict search based in: FIELD: VALUE. |
tr[]=department:foobar |
rows |
Optional |
Number of rows that query will return. |
rows=10 |
8. Customer Case Studies
8.1. Brazil
8.1.1. Insurance Company
On Intranet of Insurance Company uses OpenText WEM and OpenText Portal integrated with Dynamic Portal Module, a consolidated search was created in Viglet Turing ES, using the connectors: WEM, Database with File System. In this way it was possible to display all the contents and files of the search Intranet, with targeting rules, allowing only to display content that the user has permission. The OpenText Portal accesses Viglet Turing ES Java API, so it was not necessary to create complex queries to return the results.
8.1.2. Government Company
A set of API Rest was created to make all Government Company content available to partners. All these contents are in OpenText WEM and the WEM connector was used to index the contents on Viglet Turing ES. A Spring Boot application was created with the Rest API set that consumes Turing ES content through the Viglet Turing ES Java API.
8.1.3. University
Brazilian University website was developed using Viglet Shio CMS (https://viglet.com/shio), and all contents are indexed in Viglet Turing ES automatically. This configuration was made in content modeling and the development of the search template was made in Viglet Shio CMS.
8.2. Spanish
8.2.1. Insurance Company
Institutional website of the insurance company using OpenText Dynamic Site Module with multi languages, an integrated search was created with Turing ES, using connectors: WEM and Apache Nutch.
